Why CactusSoft Prepares Proposals
CactusSoft is a Belgian nearshoring software development company, providing full-cycle services for the Western European market. One of its primary goals is increasing profits. CactusSoft can increase profits in two ways:
- Doing our existing business more efficiently, and
- Developing our business further.
This time, we won’t be focusing on how to increase the efficiency of our existing business, but rather dwell on what we do to develop our business further.
To develop our business, we attract new clients and projects. One of the most common approaches is offering services to our existing and potential clients. In our business, we mostly offer services through proposals.
What is a Proposal?
In general, a proposal is a solicited or unsolicited plan created by one party to supply (or buy) certain goods or services to (or from) another. Unlike an offer, a proposal is not a promise or commitment. However , if it is accepted by the other party, the proposer is expected to follow through and negotiate for the creation of a binding contract. If submitted in response to a request for proposals (RFP), it normally constitutes a bid.
In the context of the article, a proposal is a set of artifacts that fully describe our business offer, technological stack, budget estimate, and how we are going to bring value to the customer.

What Is a Good Proposal?
The ultimate goal of a proposal is to start a new project that will allow us to make more profits, at least in the mid or long term, as well as enable us to create a long-term business partnership.
A good proposal is a proposal that allows us to reach this goal.
Types of Proposals
All proposals are unique, but some have a couple of things in common.
Proposal Similarities
The major common elements of proposal preparation, which are increasingly affecting your work, are strict deadlines and, as a consequence, a very fast speed of work. So, above all, your work is subject to time limits.
The reason is that in most cases we prepare a proposal while competing with other companies, and the client usually sets a specific date by which all vendors must submit their proposals.
To stay within the time limits, you need to pay special attention to some very important elements:
- Qualifications of your team members
- Management of dependencies, especially the external ones
- Speed of work, and decision making.
Proposal Differences
Despite a lot of similarities, proposal preparation can differ significantly from project to project. And when you prepare your proposal, please take into account the peculiarities of your case.
The most typical classifications of proposals are as follows:
- Goals
- Development and implementation of a new product from scratch
- Providing a service (i.e., a testing service, the third line of support service, etc.)
- Modification/development of the existing product or service (i.e., the addition of P2P transfers to the Internet-Client-Bank, modification of an encryption algorithm, migration of a frontend system from PHP to JS).
- Inputs
- Official (RFP – request for proposal, RFQ – request for quotation, RFI – request for information)
- Informal (Email / calls to account managers from the clients)
- Outputs
- ‘Classic’ proposal (a set of documents describing our vision (technical, organizational), financial conditions, and other information
- Clickable design
- Working prototype
- Number of stages
- One stage
- Several stages
- Familiarity with the client
- New client
- Existing client

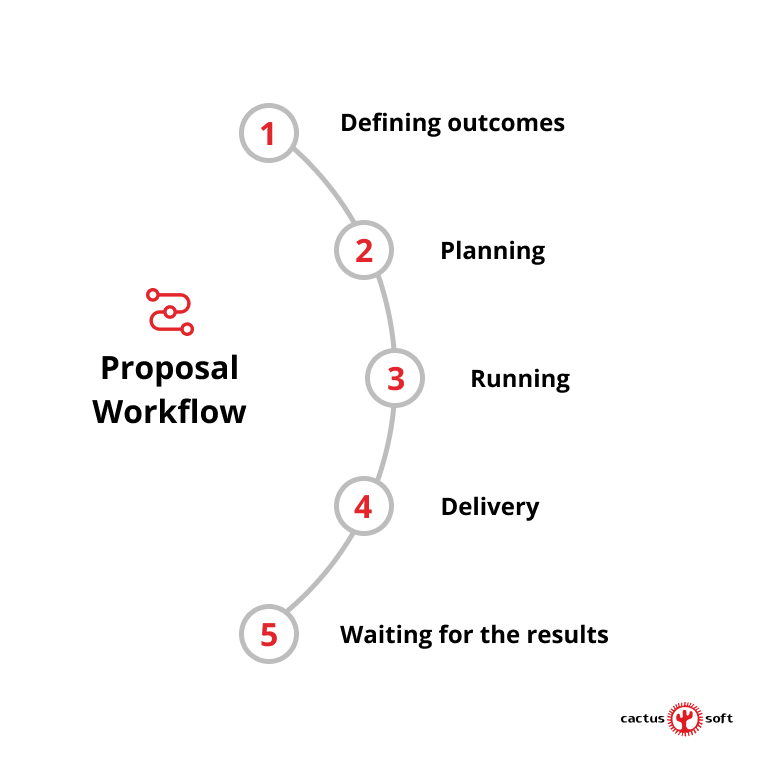
Proposal Workflow
Stage 1. Defining Outcomes
Main steps
- Gather and analyze very carefully all proposal-related information that you have received
- Communicate with the client
It’s very important to guarantee that you get all documentation updates from the client and do not miss any of them. In your communication with the clients, the most important thing is to understand their problems and context fully and correctly. This is because the deeper your understanding of your client’s business challenges, the better solution you can suggest.
It’s also important to understand the specifics of the customer’s background to make your proposal fit better:
- Try to learn everything about your future mutual work.
- Will you get access to stakeholders? To users?
- How does the internal IT department work? Do they have any formal processes? What approaches (waterfall, Agile, or other) do they use? What about the infrastructure (test environments, a code repository, external access to their network)?
- Do other vendors work with this client? How do they work together?
- Develop a single clear list of all deliverables and all requirements for each deliverable
- Spreadsheet with
- Business goals and deadlines
- Technical and software restrictions
- Assumptions
- Technical solution proposal
- Feature list with user roles, descriptions, and assumptions
- Frontend WBS (work breakdown structure) estimation (and BE, iOS, Android accordingly)
- Business WBS estimation
- Testing WBS estimation
- Design WBS estimation
- Potential risks and mitigation plan
- Project timeline
- Proposal presentation
- Cost proposal
- Spreadsheet with
Stage 2. Planning
- Staff your RFP with people who have all the required skills
At CactusSoft, tech leads, as the most experienced and skilled specialists, are assigned to RFP estimations.
- Manage risks
Every project must have risk management. Pay special attention to all risks that affect time and may cause delays:
- Manage external dependencies very carefully.
- To address risks, include time reserves in your plan explicitly.
Stage 3. Running
Proposal Algorithm
- Create a chat and add all the RFP participants.
- Schedule an RFP kick-off meeting.
- During the kick-off meeting, define the action plan and people responsible for it.
- Set a deadline for every stage of the RFP.
- BA creates a WBS (feature list).
- Tech leads estimate WBS, putting in all the assumptions and risks.
- PM validates the estimations.
- PM creates a project timeline.
- PM updates the proposal presentation.
- PM sends out
1) WBS with estimates
2) Timeline
3) Presentation to the responsible account manager.
Stage 4. Delivery
The proposal artifacts are delivered to the client.
Stage 5. Waiting for the Results
Usually, it takes some time on the client’s side to consider all received proposals from all vendors and make a decision. In some cases, the client can request additional information from you. Don’t forget to thank your team and tell them the result.
If you have an idea or a digital challenge that we can help you with, reach out to CactusSoft at info@cactussoft.biz to discuss it.