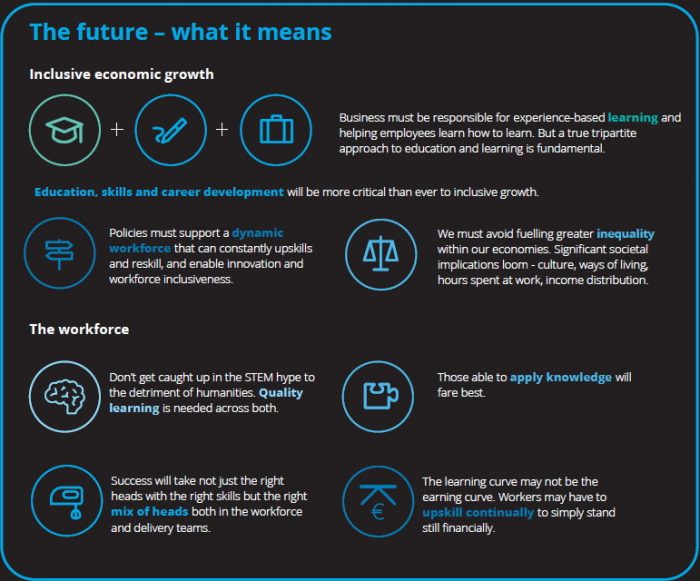
The world is moving fast! The gig economy, robotics, and cognitive technologies are impacting the workforce’s education, skills, and career development. Understanding these impacts is crucial for ensuring countries can manage the risks and opportunities for inclusive economic growth, according to Deloitte. Government, business, and society need to work together to support a dynamic workforce that is able to reskill and upskill constantly.
On the other hand, contracts, transactions, and the records of them are among the defining structures in our economic, legal, and political systems. They protect assets and set organizational boundaries. They establish and verify identities and chronicle events. They govern interactions between nations, organizations, communities, and individuals. These also have a huge impact on the workforce’s social actions and skills. And all that is needed is a strong foundation for the system.
According to Harvard Business Review, the blockchain is a foundational technology that has the potential to create new foundations for our economic and social systems. But while the impact will be enormous, it will take a long time for the blockchain to seep into our economic and social infrastructure. Let’s see how!
Why Do We Need Blockchain?
The blockchain will eliminate the need for centralized institutions like banks or governments to facilitate trade, evolving age-old models of commerce and finance into something far more interesting: a distributed, transparent, autonomous system for exchanging value. The blockchain can lower uncertainties to exchange value.
According to Don Tapscott, Co-founder of Blockchain Research Institute, the next generation Internet may be brought about by the blockchain.
The first generation of the digital revolution brought us the Internet of Information. It’s already become part of our daily life.
The second generation – powered by blockchain technology – is bringing us the Internet of Value: a new, distributed platform that can help us create the digital relationships that will reshape the world of business and transform the old order of human affairs for the better.
“The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.” Don & Alex Tapscott, authors of “Blockchain Revolution” (2016)
What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is the public registry which records who owns and transacts what in a distributed way.
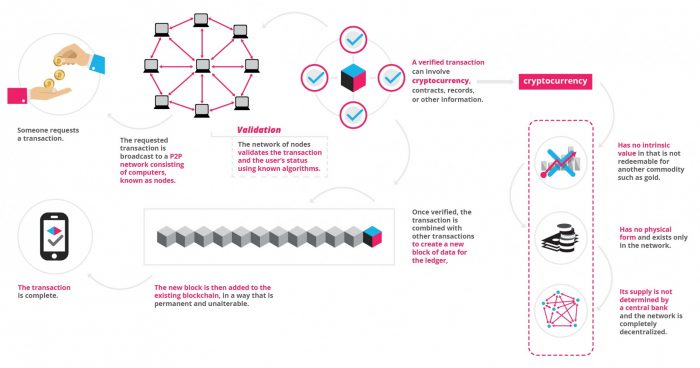
Information held on a blockchain exists as a shared and continually reconciled database. This is a way of using the network that has obvious benefits. The blockchain database isn’t stored in any single location, meaning the records it keeps are truly public and easily verifiable. No centralized version of this information exists for a hacker to corrupt. Hosted by millions of computers simultaneously, its data is accessible to anyone on the Internet.
The simplest explanation about blockchain can be found on Jamie Skella’s article “A shared record book? This doesn’t sound very complex”.
Decentralization
The blockchain is a decentralized technology.
Anything that happens on it is a function of the network as a whole. Some important implications stem from this. By creating a new way to verify transactions, aspects of traditional commerce could become unnecessary. Stock market trades become almost simultaneous on the blockchain, for instance – or it could make types of record-keeping, like a land registry, fully public. And decentralization is already a reality.
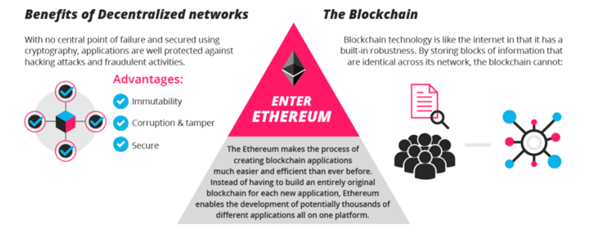
The Blockchain and Its Security
By storing data across its network, the blockchain eliminates the risks that come with data being held centrally.
According to Blockgeeks, its network lacks centralized points of vulnerability that computer hackers can exploit. Today’s Internet has security problems that are familiar to everyone. We all rely on the “username/password” system to protect our identity and assets online. Blockchain security methods use encryption technology.
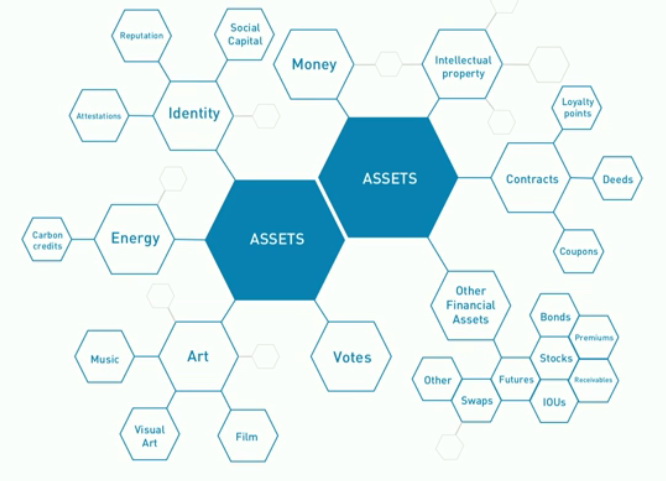
Where Will We Use the Blockchain?
The blockchain potentially cuts out the middleman for these types of transactions. The blockchain gives Internet users the ability to create value and authenticates digital information. So, what are its uses? Below are some of them.
How Does Blockchain Empower the Workforce?
I am sure that one can easily find the answer from some of the uses mentioned in the previous section: “Where Will We Use the Blockchain?”
HR and Workforce advisor and thought leader, Andrew Spence, provides his own thoughts in his article, “How Will Blockchain Impact HR?”
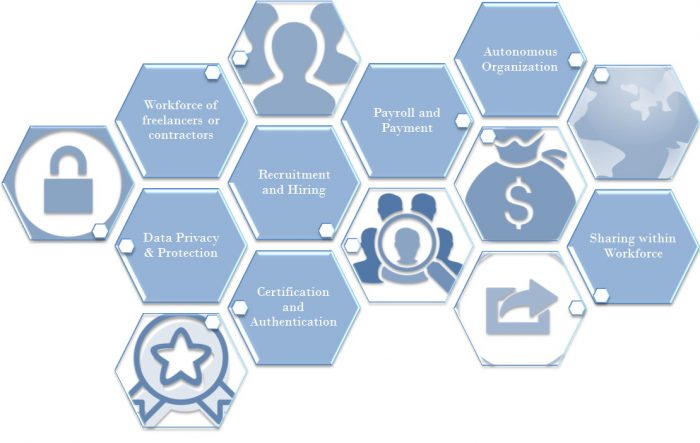
Below are some of the areas where the blockchain can play a vital role and revolutionize the future for the workforce.
Read about regulating cryptocurrency: Bitcoin and other Cryptocurrencies: Time to Regulate >>>
Workforce of Freelancers or Contractors
Andrew mentioned in his article how Chronobank.io, an Australian short-term work platform, is developing a blockchain-based financial system for freelancers or contractors to obtain work and receive payment using its own “labour-hour” token. This is surely a big step towards creating a decentralized marketplace on a new generation Internet platform for the large workforce of freelancers and contractors.
Recruitment and Hiring
Recruiters need to have access to an accurate record of the candidate’s education, employment and training. Smart contracts would be able to streamline a lot of the onboarding process, especially for high volume, high turnover positions. Education and work history verification would be the likely uses of the blockchain for the workforce.
After candidates are hired, blockchain smart contracts could also have an impact on employee wages, benefits and retirement packages. Smart contracts, the computer protocols that help to facilitate and manage the transfer of digital currency assets, are stored in a blockchain.
Data Privacy and Protection
We don’t own our data on the Internet today, which is the biggest problem in terms of data privacy. With the use of blockchain, individuals will have full control over their own data, to prevent misrepresentation. By storing data across its network, the blockchain eliminates the risks that come with data being held centrally. This is much more secure and provides a confined ownership of our own data.
Certification and Authentication
Employers face a major hiring hurdle when they need to verify information on a candidate’s resume.
“With a resume authentication database, the verification of official certificates and contracts, which have until now been typically done on paper, could be carried out using the blockchain database”.
Osamu Yonetani, CTO of Recruit Technologies.
We could also see this as a leading use of the blockchain as the education industry moves to protect the value of official accreditation in the face of its own disruption through Mass Online Open Courses (MOOCs).
This could particularly help HR when they need to validate documents such as qualifications, position history, and job experience, as well as transactional data such as a medical certificate, address changes, and tax file data.
Payroll and Payment
Sending out payroll data electronically overseas is consistently expensive for businesses and can take a long time to process due to multiple intermediary banks and third parties. Blockchain can play a significant role here.
Bitwage is one company that is taking the potential of the bitcoin in the international payments space and running with it, albeit in a targeted direction: payroll. According to Bitwage, its combination of blockchain, mobile and cloud technologies can reduce the cost of paying international employees to just 1% and yield same-day payouts for employees.
Autonomous Organization
Before the creation of Ethereum, blockchain applications were designed to do a very limited set of operations. Ethereum can also be used to build Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO).
A DAO is a fully autonomous, decentralized organization with no single leader. DAOs are run by programming code, on a collection of smart contracts written on the Ethereum blockchain. The code is designed to replace the rules and structure of a traditional organization, eliminating the need for people and centralized control. A DAO is owned by everyone who purchases tokens, but instead of each token equating to equity shares and ownership, tokens act as contributions that give people voting rights.
Sharing within the Workforce
According to Slock.it, 66% of the world are willing to share their assets for financial gain. The sharing economy’s story doesn’t end with taxis and vacation rentals. It’s expanding to touch consumers and companies, employees and employers. Slock.it is currently developing the Universal Sharing Network (USN), an open source infrastructure on which blockchain application modules can be deployed.
As there are continuous developments in the blockchain sector, the best solutions are still being devised. Ethereum provides the Blockchain App Platform. There are many projects developing several different aspects, and decentralized applications and platforms could have a considerable effect in future.
The World Economic Forum has formed a council, which will explore how the blockchain could impact industry, governments and society in the future. The world is really moving fast!
Soumyasanto Sen is an Advisor, Evangelist & Investor in HR Technologies; currently focusing on AI-driven People Analytics, Digital Strategies, Blockchain and Digital HR Transformation.
Passionate about Entrepreneurship, Co-founder & Board Member for HRTech Conscience and Delité Advisory & Partners.