Almost every aspect in the modern tech world seem to be accelerating. Most of the companies are doing their utmost to keep the pace although success rate is certainly high enough for the number of attempts ongoing. In this article The State of AI in Business 2025: The GenAI Divide | Cactus we provided some insights into this problem.
The rapid pace of change is especially evident in SaaS. New platforms appear almost daily, promising to solve the “most critical” problems across industries and markets, while others fade or are acquired within weeks. In a landscape where complexity keeps rising, how can teams realistically shorten development cycles for new products and services?
I think the answer two is twofold: there is the relentless push for “more” which is inherent in our economical system and there are new technologies that emerged to meet it. First and foremost, Artificial Intelligence, especially Large Language Models, significantly enhances the capabilities of skilled developers. Even less tech savvy individuals are now empowered to create digital products, from automated workflows to simple apps.
There is an additional source of empowerment: the availability of new tools, commonly known as “low-code” or even “no-code” tools which do not require extensive experience in coding, allowing anyone to automate workflows or build apps visually.
Low- Code tools
Let me first explain the concept behind “low-code” tools. In essence, they take the complex code normally required to provide certain functionality and package it into pre configured modules. Instead of writing everything from scratch, users can combine these ready-to-use modules, usually through a graphical interface, to solve a business problem or to create a specific workflow.
The approach of modularizing functionalities is actually not a new thing, developers have been doing it for decades. What makes low-code tools different, in my opinion, is the combination of a graphical interface and a vast library of modules. Dragging and dropping modules onto a web-based canvas and connecting them following a business logic moves problem-solving closer to the stakeholders. Technically inclined project owners can even experiment and iterate on solutions themselves, without needing a developer for every change.
So Many Tools, So Many Headaches
The acceleration mentioned earlier also affects the low-code tool landscape. There are countless tools to choose from. Take for instance a few of the ones for automation of business processes:
Picking the right one is not straightforward and depends on the specific goals to achieve, software already in use or existing systems. If, for example, Microsoft products are already used in your company and the aim is to automate processes within the Microsoft ecosystem, Power Automate might be a suitable choice. It’s even possible that the tool choice comes down to personal preferences, like slight differences in the functionality of the user interface.
Two practical examples using n8n
I just mentioned it could be hard to choose out of all the options, so why did I choose n8n to demonstrate its capabilities based on an example? There are three main reasons. The first reason is that n8n can be hosted locally, this might be an internal server or even a personal computer. Another reason is that n8n is modular in the sense that if there is a functionality you need which is not covered by the preconfigured modules (or nodes, how they are named in n8n) you can develop the functionality and integrate it to n8n. The third reason is that n8n is free to use for internal business purposes. That means there is no cost associated to the usage. There are some functionality restrictions but even with these restrictions there are many things you might automate using n8n.
Basic example: Routing emails depending on the email content
To start off with a basic example, imagine that you have a corporate email such as info@your_company.com. Assuming you have a process in place which filters out obvious SPAM emails, you want to analyze the email content and route the information to the correct person within your company so that each inquiry is noticed and processed promptly. There are several ways to set this up in n8n, but we would need at least three functionalities: a node (remember that the preconfigured modules are called this way in n8n) which checks for new messages in a given email account, a node which analyses the email content and finally a node which sends an email to the person in charge.
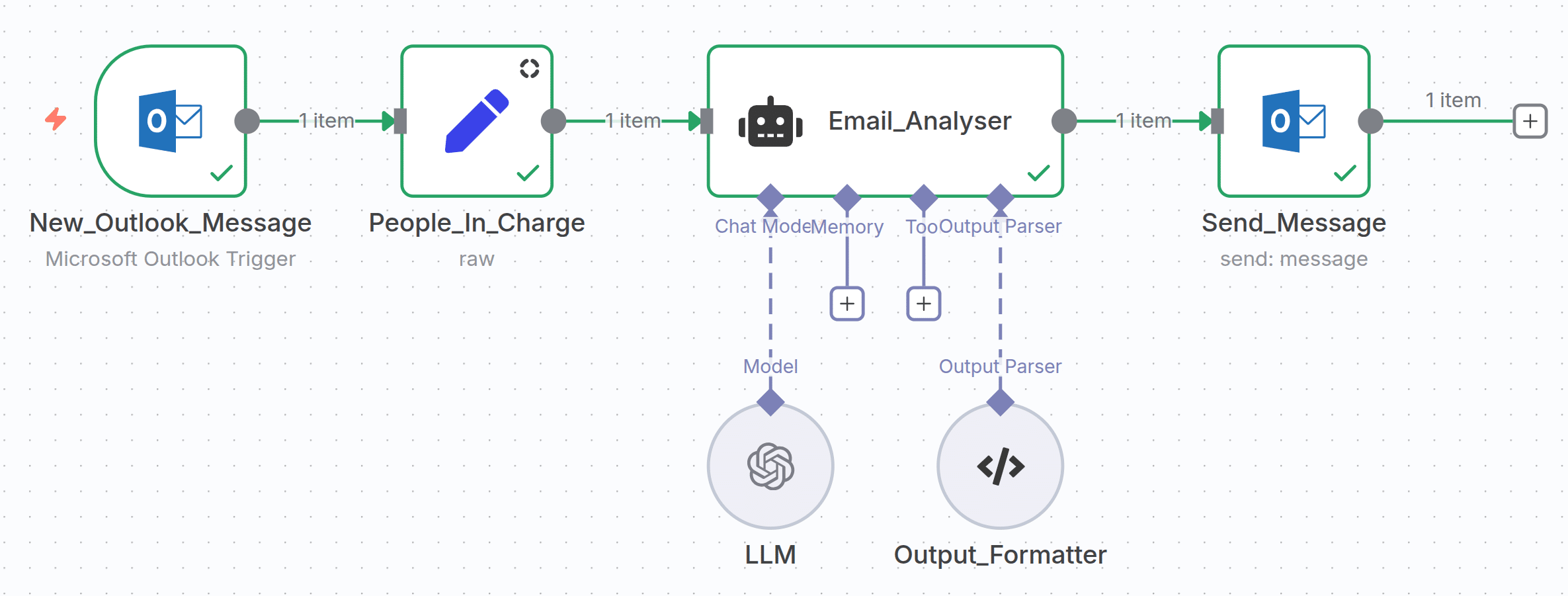
That’s what this would look like in n8n:
Let’s take a look at each node and its functionality:
New_Outlook_Message:
This is the event which triggers the workflow. In this example the email account is checked periodically for new messages. The basic message details such as email subject, received date, sender and the email content are forwarded to the next node.
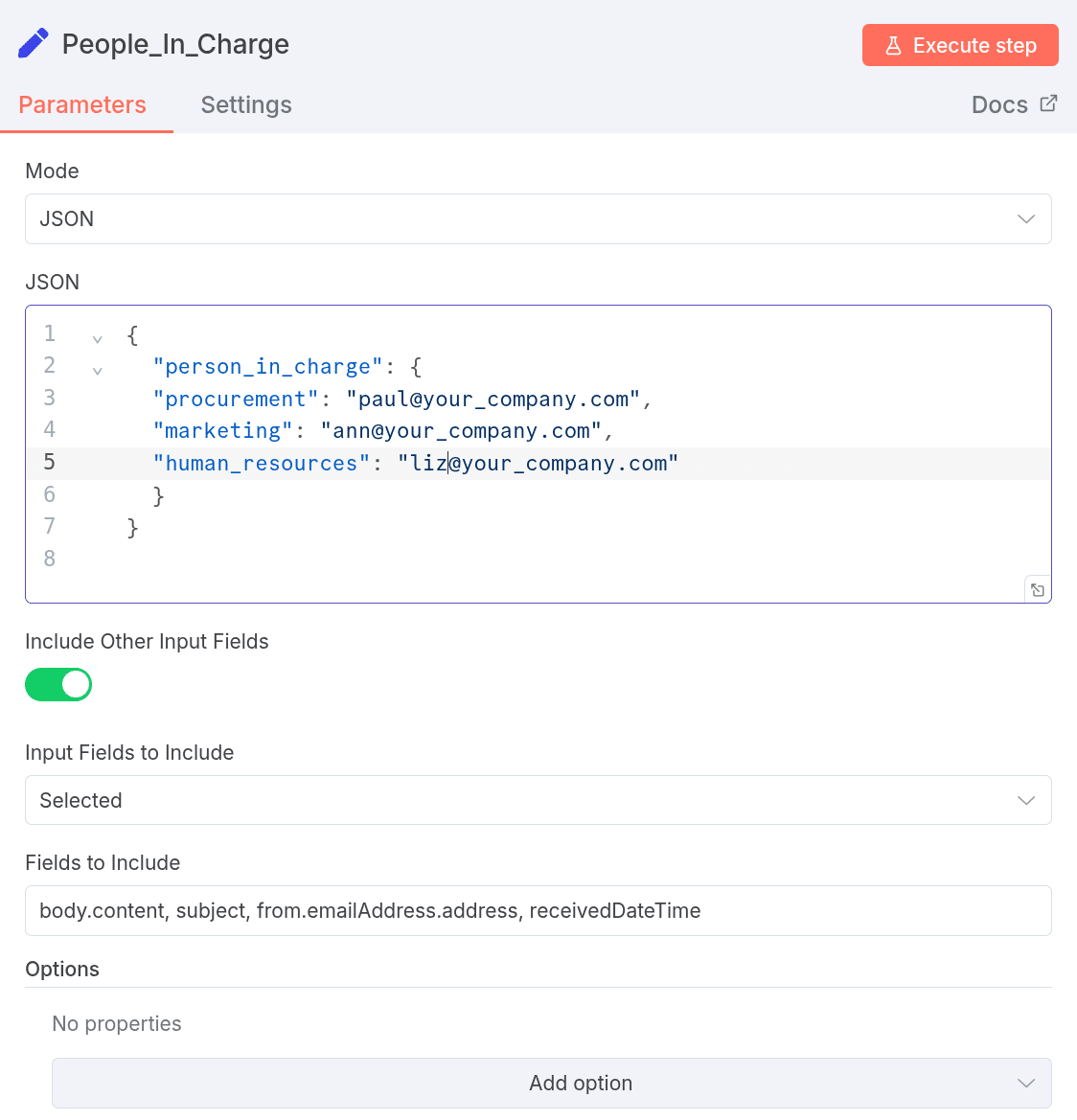
People_In_Charge:
This node contains static information about the person in charge for each department. Within n8n, this looks like this:
Email_Analyser:
This is where the content of the email gets analyzed. In this case I opted for the Agent node which orchestrates Large Language Model (LLM) calls and reasoning. At this point it’s important to notice, that in order to use this the Agent node, you need to specify the LLM you want to use. Providers might be openAI, Anthropic, Gemini or any other. Within n8n you connect to the service via the corresponding API-key. The terms of use of the corresponding provider apply. If the email content has specific requirements concerning data privacy, users could opt for Azure OpenAI or even Ollama which is usually deployed locally. In addition to the LLM, I provided the agent node with an Output_Formatter. This is not mandatory but increases the reliability of the LLM outputs as it forces the LLM to respond in a structured way rather than free text.
Send_Message:
Once the Agent node has finished with the analysis, it forwards the information to the last node in which the email gets formatted and finally sent to the person in charge.
Advanced example: Automating a typical back office process – order intake
Imagine you’re the person in charge of order intake in your company. It is not uncommon that this process starts with an email. The email needs to be read, attachments opened and information extracted. Processing the order might involve tasks such as checking product availability in a database or documenting it in a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. All this, in principle, can be automated using n8n.
However, to make such an automation reliable, certain technical understanding becomes essential. The incoming email might include different types of attachments such as images, PDFs, or spreadsheets. Each of these attachments has to be parsed differently, to extract information from the attachments custom nodes or even scripts might be required. Finally, an Agent node might be used to interpret and structure the extracted information before creating the order record in your system. Agent nodes typically use specific instructions redacted in natural language. The quality of these instructions have an impact on the agent behavior.
At this stage, the line between low-code and traditional development starts to blur. While the graphical interface and prebuilt nodes still accelerate the development process, a technical understanding of what happens under the hood becomes increasingly important.
Conclusion
Low-code tools like n8n can speedup development cycles and empower people who might have never written a line of code to automate basic business processes. What needs to be considered, though, is that automation does not eliminate complexity, it just moves it somewhere else. Automating more advanced business processes will require more complex flows and most likely will require a deeper technical understanding of how to connect preconfigured nodes or even develop custom nodes.
Thats where experience makes a difference. At Cactus we help organizations to set up low- code tools like n8n, and design and implement automation processes that actually work in their specific context.